HPV often practically does not manifest itself in any way. The main symptoms of human papillomavirus are, of course, warts, which can appear in the most unexpected places: on Organs genitals, palms, arms, neck and other parts of the body. Read more about the hidden manifestations of this virus and methods of treatment in the following article.
What is human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the common name for more than 70 different viruses that can cause disease in various human organs: some of the HPV viruses cause skin diseases, others cause genital warts (genital warts) and other diseases of Organs genital organs. Each of the viruses in the HPV group has its own sequence number and differs from other viruses in its unique DNA composition.
Currently, the role of certain types of human papillomaviruses in the development of malignant tumors of various organs has been proven: for example, cervical cancer, penile cancer, throat cancer, etc. Different types of human papillomavirus are divided into groups depending on their ability to cause malignant neoplasms. Thus, it is customary to distinguish between viruses with high, medium and low oncogenicity (oncogenicity is the ability of a virus to cause cancer). Viruses with high oncogenicity include HPV 16 and 18, tk. they are most often found in cervical cancer.
How does HPV enter the body
The most common form of human papillomavirus (HPV) transmission is sexual contact, which is why this infection is classified as a group of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Also, infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is possible through contact of damaged skin or mucous membranes with secretions of a sick person (for example, underwear, towels, etc. ). Transmission of human papillomavirus from mother to child during childbirth is possible.
Analyze
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common viral infection of the genital tract. Most sexually active men and women are infected at some point in their lives, and some can become reinfected.
The peak period for acquiring the infection for both men and women begins immediately after they become sexually active. HPV is sexually transmitted, but penetrative sex is not necessary to transmit the virus. Skin-genital contact is a well-established route of transmission.
Many types of HPV do not cause problems. HPV infections usually clear up on their own without any intervention within a few months of acquiring it, and about 90% clear up within 2 years. A small proportion of infections with certain types of HPV can persist and progress to cancer.
Cervical cancer is by far the most common disease associated with HPV. Almost all cases of cervical cancer can be caused by HPV infections.
Despite limited data on anogenital cancers other than cervical cancer, a growing body of evidence links HPV to cancers of the anus, vulva, vagina, and penis. Although these cancers are less common than cervical cancer, their association with HPV makes them potentially preventable using the same primary prevention strategies for cervical cancer.
HPV types that don't cause cancer (especially types 6 and 11) can cause genital warts and respiratory papillomatosis (a disease in which tumors grow in the airways from the nose and mouth to the lungs). And while these conditions rarely lead to death, they can often lead to illness. Genital warts are common and highly infectious.
How HPV is transmitted and manifests itself
In modern medical science, more than 150 types of viruses have been identified. Depending on the type, it affects the functioning of all organs and systems of the human body. For example, infected people notice various neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of genital warts and wart-like growths.
The main route of transmission is physical contact with the carrier, including sexual intercourse without a condom. But it is also quite common to get infected through household means. Usually, after entering the body, the infection does not manifest itself in any way, so people do not even know that they are carriers.
How does papillomavirus infection manifest itself?
The most common manifestations of human papillomavirus infection are:
- Pointed warts. The development of genital warts and papillomas is most often caused by oncogenic low-risk HPV. Condylomas are single and focal, they often occur in places that are injured during intercourse. The size of the elements is from 1 millimeter to several centimeters, they resemble a "cockscomb" or "cauliflower" shape and are located on a narrow base (leg). Most often, women find warts to the touch during washing, which are felt as an unevenness. With a large number or size of genital warts, they can be sore and bleed, interfere with normal sex life and childbirth, and cause psychological discomfort. Itching rarely accompanies the manifestations of human papillomavirus infection.
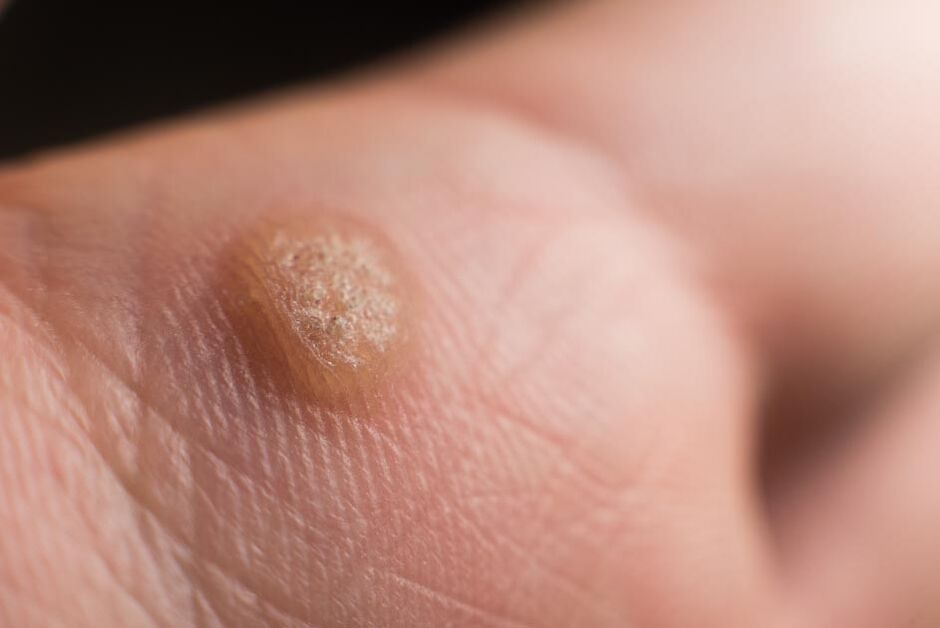
- Papillomas (warts). Unlike papillomas of a tumor nature, viral papillomas appear, disappear and reappear, since their severity depends on the state of the organism's defenses at the time. Viral papillomas do not differ in color from normal skin and can grow anywhere.
- Flat condyloma of the cervix. Condyloma plano is a manifestation of a chronic and long-lasting viral infection that causes changes in the cells of the epithelium of the cervix. It can be combined with genital warts on the external genitalia. Changes in the cervix, characteristic of HPV, always alert the doctor, as women who have this virus for a long time are 65 times more likely to contract cervical cancer than those who do not. However, the presence of a high-risk virus in the body does not mean that a woman will definitely get cancer. It is necessary to have additional factors so that the cells can degenerate into malignant ones. The fact of detecting high-risk virus types gives the patient a significant advantage in the fight against the disease; here the formula "forewarned is forearmed" is most appropriate. Thus, the average age of women with the first signs of malignant transformation in the cervix is 30 years, and the average age of patients with cervical cancer is 50 years.
HPV signs in women
In women, human papillomavirus infection can cause the appearance of genital warts - genital warts, which in many cases are found only during a gynecological examination.
They grow back about three months after infection. Most often they are formed on the labia minora, in the vagina, on the cervix, cervical canal, on the skin around the anus.
Outwardly, these are small formations located on a wide "leg" with jagged edges. At the same time, those types of HPV that cause genital warts are not the ones that cause cancer.
Symptoms of the disease in women also include cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - a precancerous condition of the uterine mucosa, which provokes violation of cell maturation. At the moment, doctors know of three stages of this disease, two of which are not particularly dangerous, and the third is the first stage of cervical cancer. Similar symptoms are caused by viruses of types 16 and 18. In addition, cancer is caused by types 31, 33, 35 and 39.
Symptoms of HPV in women and men can include the presence of small growths not only on Organs genitals, but also in other places - under the mammary glands, in the armpit, on the neck and on the eyelids.
For men, the disease is less dangerous than for women. And if some carcinogenic types of the virus that cause the development of outgrowths on the skin of a man rarely provoke tumors in the stronger sex, then a woman, having contracted them from a man, is at risk of developing cervical cancer.
the course of pregnancy
During pregnancy, visible warts often reappear, tend to increase significantly, become loose, large formations can cause difficulties during childbirth. There is evidence that primary HPV infection during pregnancy can lead to a threatened miscarriage, but whether such an infection causes malformations in the fetus is a moot point.
The frequency of transmission of HPV from mother to fetus, according to different researchers, varies quite significantly - from 4 to 80%. It is still not known exactly how the virus is transmitted. It is more likely through the cervical canal and fetal membranes upwards or by contact as the child passes through the mother's birth canal.
Recently, the development of papillomatosis of the larynx, trachea and bronchi and anogenital warts in infants has been associated with HPV infection during childbirth. The disease is quite rare, in addition, cases of this disease have been described in children born by cesarean section, therefore the presence of HPV and its manifestations in pregnant women is not an indication for cesarean section.
An indication for surgery can only be the presence of a giant condyloma, which makes it difficult to give birth through the natural birth canal. But these condylomas occur only in women with severe immunodeficiency, such as AIDS.
After childbirth, HPV detected during pregnancy is usually not detected, and the clinical manifestations in the form of massive growths significantly decrease or disappear. It should be noted that HPV detected for the first time during pregnancy, as a rule, is not detected after childbirth.
Risk factors for cervical cancer
- first sexual intercourse at an early age;
- multiple sexual partners;
- tobacco use;
- immunosuppression (eg, people infected with HIV are at increased risk of HPV infection and are infected with a wide variety of HPV types).
Diagnosis
The primary method for diagnosing PVI is a routine clinical examination. To confirm this diagnosis, colposcopy is used (examination of the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina with a special magnifying glass) and cytological examination (for this, a scraping of the cervical canal and the surface of the cervix is taken).
Cytological examination does not reveal the virus itself, but changes in the cells of the epithelium of the cervix that are characteristic of this infection. A histological examination helps to clarify the cytological diagnosis: in this case, not a scraping of surface cells is taken, as in cytology, but a piece of tissue, and not only the structure of cells is studied, but also the correct arrangement of their layers . During pregnancy, a biopsy is usually not performed.
To determine the types of viruses and their oncogenic risk, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used, which determines the DNA fragments of the pathogen. It allows you to accurately determine the presence of the HPV virus in the cervix. This is important for the prognosis of developing cervical diseases.
hpv treatment
Since it is currently impossible to achieve a complete cure from human papillomavirus infection (along with this, spontaneous and spontaneous recovery is often observed), the manifestations of HPV are treated, and not the presence of the virus in the body. At the same time, the effectiveness of various methods of treatment is 50-70%, and in a quarter of cases, the disease reappears a few months after the end of treatment.
Given the possibility of self-resolution of genital warts, it is sometimes advisable not to carry out any treatment. The question of adequacy of treatment for each pregnant patient is decided individually.
In this case, it is necessary to avoid factors that lower immunity (hypothermia, severe emotional stress, chronic overwork, beriberi). There are studies showing the preventive effect of retinoids (beta-carotene and vitamin A), vitamin C and micronutrients such as folate on HPV infections.
The most commonly used treatments for genital warts are:
Destructive Methods
Destructive methods are local treatments aimed at removing genital warts. There are physical (cryodestruction, laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, electrosurgical excision) and chemical (trichloroacetic acid) destructive methods, as well as surgical removal of genital warts.
In pregnant women, destructive physical methods and trichloroacetic acid preparations can be used. Treatment with destructive methods is desirable to carry out only in the early stages of pregnancy, with special care. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the risk of possible side effects during treatment (bleeding and secondary infection due to impaired blood circulation, toxic complications) and the possibility of reappearance of genital warts after their removal.
cytotoxic drugs
Cytotoxic drugs are STRICTLY CONTRAINDICATED during pregnancy. For women of reproductive age, reliable contraception or abstinence from sexual activity during treatment is recommended.
immunological methods
Interferons are most commonly used to treat HPV infection. They are a family of proteins that are produced by immune system cells in response to viral stimulation. Immunoglobulin preparations are used in conjunction with topical application of drugs. These drugs are actively used at the end of pregnancy. However, in 60% of cases, even long-term interferon therapy does not lead to clinical improvement and does not prevent fetal HPV infection.
Specific antiviral drugs
specific antiviral drugs. These drugs are not used in pregnant women with papillomavirus infection because of insufficiently studied effects on the fetus. By the way, the well-known antiviral drug has no effect on HPV.
Summary
- Itching can be caused by PVI, but to confirm this cause, all other possible contact-borne causes of itching must be excluded. This is not an STD, and the infection may not necessarily come from a sexual partner and not necessarily from sex life. Condom, virginity, regular sexual partner, abstinence - do not mean the impossibility of contracting PVI.
- HPV is widespread, its detection in the body is more of a pattern than an oddity.
- PVI is diagnosed "by eye", according to clinical manifestations, and not by PCR.
- If PVI is detected, a colposcopy is required, if necessary, a biopsy and treatment. If you can give up OK from the external genitalia and not treat, then the cervix must be examined and treated without fail. PVI is the most common cause of cervical cancer.
- If HPV is detected, an examination of the partner is necessary, as penile cancer is the same consequence of PVI as cervical cancer. The exam is also ophthalmological, not PCR.
- Manifestations of PVI - OK or flat condyloma - and not the presence of the virus in the body are subject to treatment.
- The first stage of treatment is conservative. The basis of therapy is antiviral drugs, incl. - locally. Immunomodulators are an auxiliary and optional component of treatment.
- Itching can be caused by PVI, but all other possible causes of itching must be excluded to confirm this cause.
- PVI recurs with a decrease in immunity. This does not indicate the ineffectiveness of the previous treatment. No treatment can completely remove the virus from the body and does not guarantee complete elimination of OK.
- PVI can be transmitted during childbirth from mother to child, causing laryngeal papillomatosis. This is easily treatable. Condylomatosis is not an indication for cesarean section.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) can be in a woman's body for years and not manifest itself in any way, constantly endangering the risk of developing cancerous and precancerous diseases of its "mistress".


















